Vue form bundle
Installation
tbc.
Configuration
tbc
How it works
First we have to discuss, what is the problem with Symfony forms and vue.js (or any other javascript based rendering library). In Symfony we have a quite mighty form api which help us to translate a model into a form with view data, which can be used with the twig engine to render a html form. On the other hand the form api can use the input from a request to translate it back to our model with changed data.
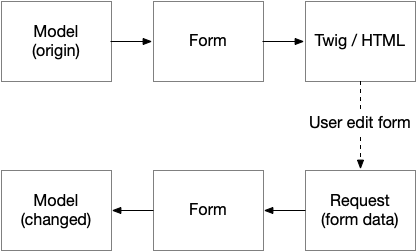
If we use a javascript rendering library like vue, we will generate the html code with this library on the client side, so we are not able to use the provided twig functions by symfony. We have to replace this part with our own solution. This bundle and the corresponding js package provide a solution and give us a small api to extend the behavior for your own forms.
Let's have a closer look into how symfony is handle the things with twig and how this bundle is working.
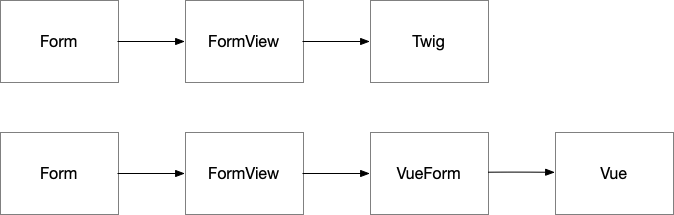
On the top of the above image you can see the Symfony workflow. The Form will create a FormView which will be used by twig. The FormView contains all necessary data to render the form. For our workflow we will use the FormView and create our vue data out of it. The data is normalized array, that can be passed to the client.
Here is a small code example to show how easy it is to use the VueForm inside a controller.
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Form\MyForm;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\AbstractController;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\JsonResponse;
class HelloController extends AbstractController
{
public function __construct(
private VueForm $vueForm,
)
{
}
public function formAction()
{
$form = $this->formFactory->create(MyForm::class);
$formData = $this->vueForm->createData($form->createView());
return new JsonResponse(['form' => $formData])
}
}FormTypeExtension
We use FormTypeExtensions to enrich our FormView with data we need for our vue application.
namespace Enhavo\Bundle\VueFormBundle\Form\VueType;
use Enhavo\Bundle\VueFormBundle\Form\AbstractVueTypeExtension;
use Enhavo\Bundle\VueFormBundle\Form\VueData;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormView;
class TextVueTypeExtension extends AbstractVueTypeExtension
{
public function buildVueData(FormView $view, VueData $data, array $options)
{
$data['component'] = 'form-simple';
}
}Note
In contrast to build the variables in the FormView with twig we have to take care what kind of data we will expose, because this data can be read by the user.
Client side
On the client side we can use the output from our controller to render the view in the browser.
// entrypoint
import {createApp, reactive} from "vue";
import {FormFactory} from "@enhavo/vue-form/form/FormFactory";
import VueForm from "@enhavo/vue-form/index";
import ApplicationComponent from "./component/Application";
let formFactory = new FormFactory();
fetch('path/to/controller/action')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => {
let form = formFactory.create(data.form);
const app = createApp(ApplicationComponent, {
form: reactive(form)
});
app.use(VueForm);
app.mount('#app');
});The VueForm plugin provide components similar to the twig function from Symfony.
<template>
<!-- like {{ form(form) }} in twig -->
<form-form :form="form" />
<!-- like {{ form_row(form.property) }} in twig -->
<form-row :form="form.get('property')" />
<!-- like {{ form_widget(form.property) }} in twig -->
<form-widget :form="form.get('property')" />
<!-- like {{ form_label(form.property) }} in twig -->
<form-label :form="form.get('property')" />
<!-- like {{ form_errors(form.property) }} in twig -->
<form-errors :form="form.get('property')" />
<!-- like {{ form_help(form.property) }} in twig -->
<form-help :form="form.get('property')" />
</template>Listener
The vue forms have also their own listener sub system. To listen and fire custom events and to build a more consistent event system. To add a listener on form we recommend to use visitors. Inside a visitor you are able to add the current form (or any other) to the listener.
import {AbstractFormVisitor} from "@enhavo/vue-form/form/FormVisitor"
import {FormEventDispatcher} from "@enhavo/vue-form/form/FormEventDispatcher"
export class MyCustomVisitor extends AbstractFormVisitor
{
constructor(
private formEventDispatcher: FormEventDispatcher,
) {
super();
}
supports(form: Form): boolean
{
return form.componentVisitors.indexOf('my_custom') >= 0;
}
apply(form: Form): Form | void
{
this.formEventDispatcher.on('change', (event: ChangeEvent) => {
// Do something if this form has changed, e.g. hide a child if value is changed.
// Don't use the form var from outside this scope, always use the event and retrieve the form from it,
// because the outside form may not be reactive and thus changes might have no effects!
if (event.form.getValue() === 'something') {
event.form.parent.get('myChild').visible = false;
}
}, form.get('field'));
}
}Visitors
Before vue is loading the form data, you are able to make changes to the form data. To do so, you can add a FormVisitor object. A visitor implements FormVisitorInterface, that require a support and apply function. In the support function you have to return a boolean if the apply function should be used for this form child. Inside the apply function you can make changes on the child e.g. add an attribute or change the component.
You can add the visitor to the FormFactory, so every time the form will be created, the visitor is applied to the form data.
import {createApp, reactive} from "vue";
import {FormFactory} from "@enhavo/vue-form/form/FormFactory";
import {FormVisitor} from "@enhavo/vue-form/form/FormVisitor";
import {Form} from "@enhavo/vue-form/model/Form";
let formFactory = new FormFactory();
formFactory.addVisitor(new FormVisitor(
(form: Form) => {
return form.component == 'form-choice' && !form.expanded;
},
(form: Form) => {
form.attr.class = 'my-class'
},
);
let data = {}; // get data somewhere
let form = formFactory.create(data.form);Apply visitor to FormType
Instead of checking the component inside the supports function. You can also check the componentVisitors property and apply the visitor to a predefined string.
let formFactory = new FormFactory();
formFactory.addVisitor(new FormVisitor(
(form: Form) => {
return form.componentVisitors.indexOf('custom_visitor') >= 0; // you can also check for a name, component or value
},
(form: Form) => {
// do something
},
));In the form builder definition you are able to apply that visitor to your form.
public function buildForm(FormBuilderInterface $builder, array $options)
{
$builder->add('name', TextType::class, [
'component_visitors' => ['custom_visitor'],
]);
}